The increasing use of internet demands very high bandwidths. High speed data sharing and multitasking across multiple platforms at home requires great capacity and one way to fulfil this capacity is to bring optical fiber to the home.
Fiber-optic communication is based on the principle that light in a glass medium can carry more information over longer distances than electrical signals can carry in a copper or coaxial medium or radio frequencies through a wireless medium.
The purity of today's glass fiber, combined with improved system electronics, enables fiber to transmit digitized light signals hundreds of kilometers without amplification. With few transmission losses, low interference, and high bandwidth potential, optical fiber is an almost ideal transmission medium.
Fiber to the home (FTTH) configuration is the most suitable to meet the speed requirements of today. FTTH provides the highest speeds and a future-proof network infrastructure.
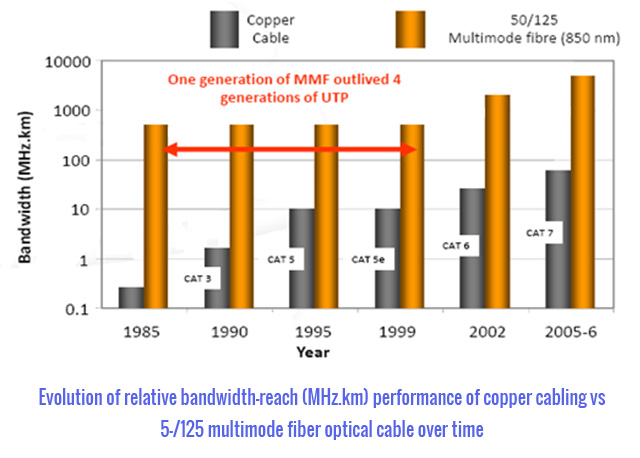
Why Fiber over Copper?
Types of fibers
| Fiber Type | Core Diameter | Cladding Diameter | ITU-T Standards |
| OM1 | 62.5 microns | 125 microns | As Per TIA/EIA |
| OM2 | 50 microns | 125 microns | G-651.1 |
| OM3 | 50 microns | 125 microns | G-651.1 |
| OM4 | 50 microns | 125 microns | G-651.1 |
| OS1 or OS2 | 8 to 9 microns | 125 microns | G-652 or G-652D |
| SM Bend Insensitive | 8 to 9 microns | 125 microns | G-657 |
Plicing is the process of joining two fibers together
Other important parts
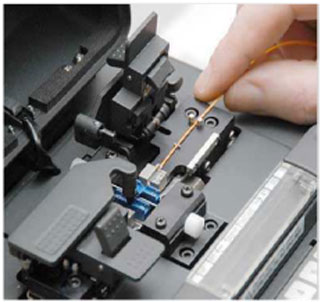
Multifiber Connectore (MTP Systems)
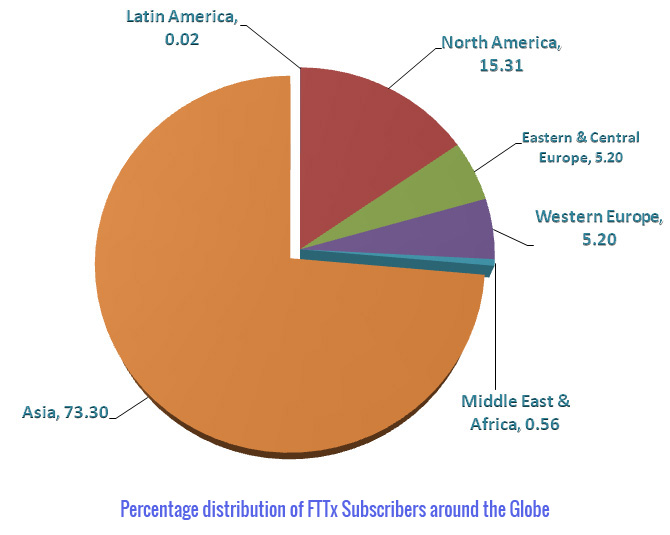
Asia continues to make strides in the FTTX market
Asia's FTTH subscriber base is clustered around Japan, South Korea, China, Taiwan and Hong Kong
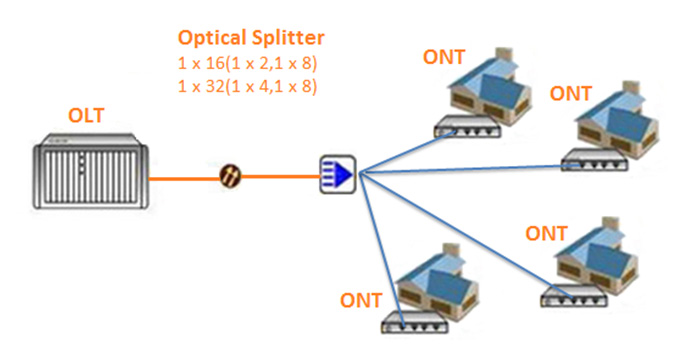
There are two popular architectures used with FTTH
Point to multipoint FTTU network
Gigabit Passive Optical Network (GPON) is the leading FTTH standard. Its main characteristic is the use of passive splitters in the fiber distribution network, enabling one single feeding fiber from the provider's central office to serve customers in multiple locations
GPON technology has the active network elements OLT (Optical Line Termination) at the central office and ONT (Optical Network Termination) at the subscriber site. Typical GPON configuration consists of a single PON port at the OLT and a number of ONTs connected to it over a single fiber feeder.
GPON has a downstream capacity of 2.488 Gb/s and an upstream capacity of 1.244 Gb/s which is shared among users. Encryption is used to keep each user's data secured and private from other users.
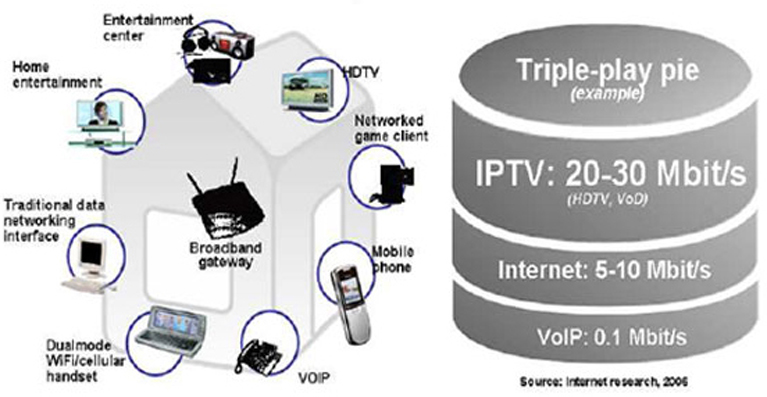
Today's Applications: "Triple Play"
True triple-play services require bandwidth from 25 to 100 Mbit/s to the subscribers
FTTH Evolution
Major PON Technologies and Properties
| Characteristics | EPON | BPON | GPON |
| Standard | IEEE 802.3ah | ITU-T G.983 | ITU-T G.984 |
| Protocol | Ethernet | ATM | Ethernet, TDM |
| Rates (Mbps) | 1250 down.1250 up 8b10b-encoded | 622 down, 155 up | 2488 down, 1244 up |
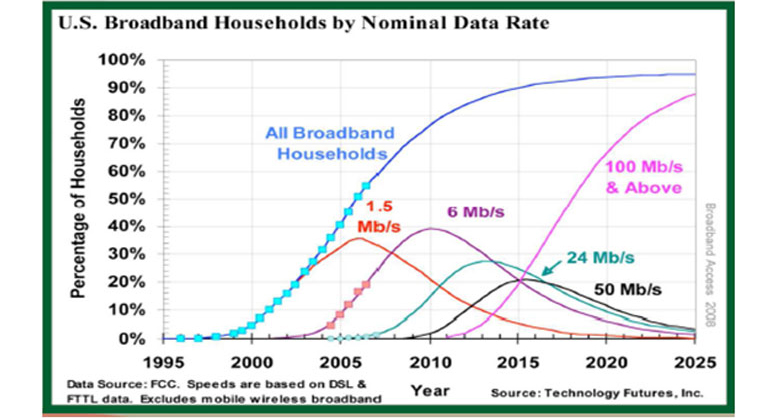
Future Trends: Bandwidth requirements are increasing rapidly
Vendor Eco-System



Our Offering
We offer projects and solutions in all types of FTTX applications and provide high quality products. We are a systems integrator. We understand that every system is different and has different requirements and therefore, provide customized solutions tailored to every kind of network and build.
| Areas of specialization | Key Markets | We deliver |
| Connectivity and Optical Passive Devices | Telecom (Datacenter, FTTX, Long Haul, Metro) | Our solutions help you build an affordable and reliable communication infrastructure for the present as well as the next generation |
| Fiber Management Systems | Datacom | Our product concepts are developed working with installers and backed by more than a decade of manufacturing experience |
| Optoelectronic Components and Subsystems | FTTA | We customize our support based on understanding your requirements and strive to be a part of your success story |
| Structured Cabling and Solutions | Security | |
| Equipment & Instruments | Network Performance Monitoring |